All eyes will be on the skies Friday for views of a total solar eclipse, expected to be spectacular only from Norway's Svalbard archipelago and Denmark's Faroe Islands.
A partial eclipse of varying degrees should also be visible, weather permitting, across most of Europe, northern Africa, central Asia and the Middle East.
On Friday, the moon’s shadow will alight on Earth’s surface at 0741 GMT in the eastern central Atlantic, according to Britain’s Nautical Almanac Office.
Die-hard eclipse junkies have flown in to the Faroe Islands, a Danish autonomous territory, and Norway’s Arctic Svalbard archipelago from around the world to observe the less than three minutes of daytime darkness, a phenomenon that has fascinated mankind since the beginning of time.
More than 8,000 visitors were expected in the Faroes, where the total eclipse is due to begin at 9:41 am (0941 GMT), and some 1,500 to 2,000 were expected in Svalbard, where it should start at 11:11 am (1011 GMT).
“There are a lot of eclipse chasers from all over the place,” Torstein Christiansen from the Faroese tourist office told AFP.
“The majority are from Europe but there are also countries which are not usually on our list, like Australia, New Zealand, the (United) States, Africa,” he said.
Meanwhile, a group of 50 Danes have bought tickets aboard a Boeing 737 chartered by a science magazine to watch the event from the skies above the Faroe Islands.
The threat of polar bears
In Svalbard, which is just emerging from four months of winter darkness, hotels have been fully-booked for years ahead of the event, the 10th solar eclipse of the 21st century.
In the Arctic archipelago, where everything is extreme, visitors must contend with temperatures as low as -20 Celsius (-4 Fahrenheit) at this time of year.
And then there’s the threat of roaming polar bears.
A Czech tourist who was slightly injured in a polar bear attack on Thursday served as a reminder of the real danger posed by the animals, which have killed five people since 1971 in Svalbard.
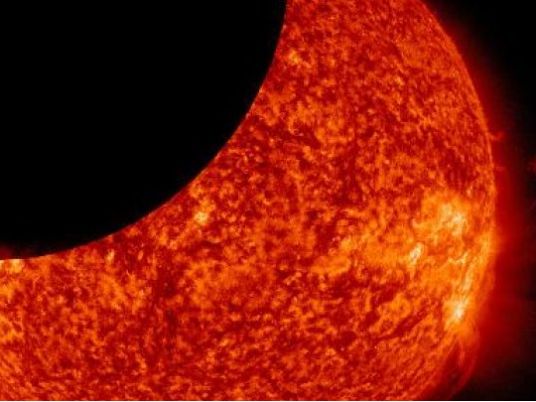
Total eclipses occur when the moon sneaks between Earth and the Sun, and the three bodies align precisely.
The moon as seen from Earth is just broad enough to cover the solar face, creating a breath-taking silver halo in an indigo sky pocked by daytime stars.
Elsewhere, the eclipse will be partial, to varying degrees: the sun will 97 percent hidden in Reykjavik, 93 percent in Edinburgh, 84 percent in London and 78 percent in Paris.
In places like London and Paris, observers won’t get much of a sense of darkness.
“It won’t get very dark because even at 20 percent, the sun still brightens up (the sky) a lot,” Patrick Rocher of the IMCCE astronomy institute in France told AFP.
“What will be different is that the light will come from a crescent-shaped sun,” he said.
The next total solar eclipse visible from Europe is not due until August 12, 2026.
Another celestial phenomenon is also expected on Friday.
Earth’s satellite will appear as a “supermoon,” which happens at its closest point to our planet, its perigee.
This, and the moon’s alignment with the sun, will add to the gravitational pull on the seas—creating what is literally a high point in the 18-year lunar cycle.
“The eclipse and the tide are linked,” says Kevin Horsburgh, head of the Marine Physics and Ocean Climate research group at Britain’s National Oceanography Centre (NOC).
“For an eclipse to take place, the sun, the Earth and the moon need to be in a straight line, which is also an essential condition for high tides.
“And for particularly big tides, the moon needs to be directly overhead at the equator at the time.”
The celestial ballet will on Saturday result in major tides most perceptible in Canada’s Bay of Fundy, on the French Atlantic coast, in the English Channel and North Sea—but even the Mediterranean will feel the difference.


